4 Practical Ways to Build an AI Chatbot for Your Website
4 Practical Ways to Build an AI Chatbot for Your Website
AI chatbots have rapidly evolved from simple website widgets into core digital interfaces for modern businesses. Today’s chatbots answer customer questions, retrieve enterprise knowledge, trigger workflows, and even hold real-time voice conversations.
Yet, many teams struggle because the term “AI chatbot” is used to describe very different systems. The right approach depends less on tools and more on capabilities.
In this blog, we outline four practical ways to build an AI chatbot for your website, using a capability-driven lens that helps you choose the right architecture without getting lost in feature lists or vendor comparisons.
A Simple Capability Lens
All modern chatbots are powered by large language models (LLMs). What differentiates them is not the model itself, but three core capabilities:
- Knowledge grounding – Does the chatbot retrieve answers from your data?
- Actions – Can it trigger workflows or interact with systems?
- Modality – Does it support text only, or real-time voice as well?
Using this lens, chatbot approaches naturally fall into four clear categories.
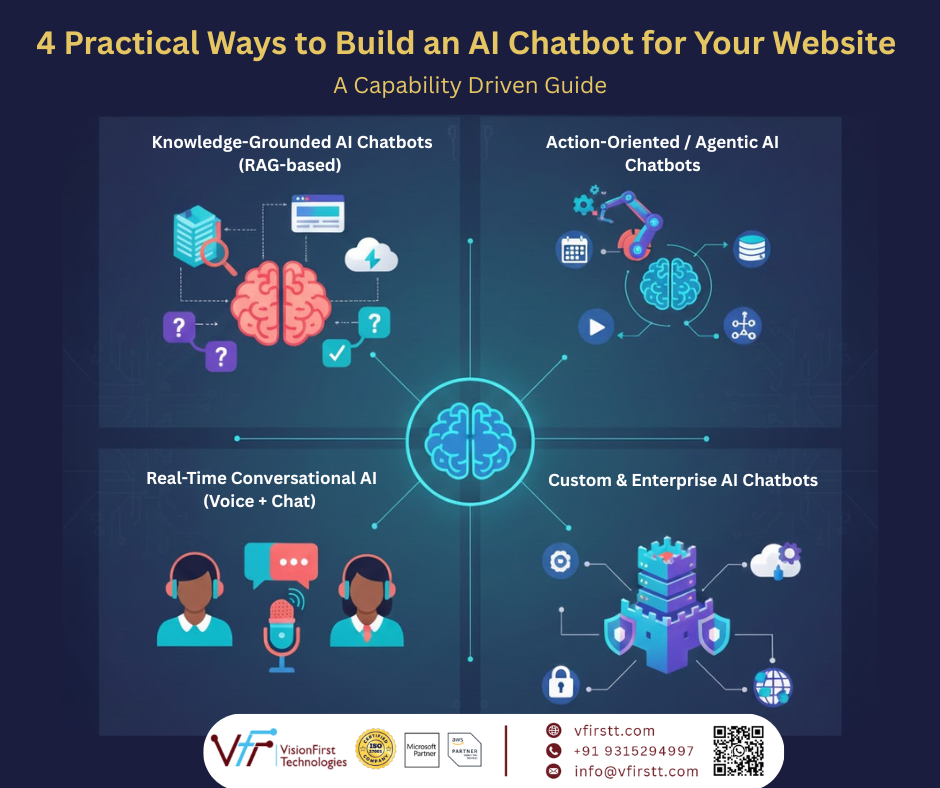
1. Knowledge-Grounded AI Chatbots (RAG-based)
Knowledge-grounded chatbots are the most common entry point into GenAI solutions for enterprise use cases.
These chatbots use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to answer questions based on your website content, documents, PDFs, or internal knowledge repositories. The chatbot retrieves relevant information using vector search and generates responses grounded in that data.
This approach is widely used for:
- Website FAQs
- Product documentation
- Internal knowledge portals
- Enterprise LLM knowledge retrieval use cases
Examples
- Chatbase
- Botpress (knowledge-base mode)
- Custom RAG chatbot using vector databases
This category often involves vector database implementation services and forms the foundation for many RAG application development projects.
2. Action-Oriented / Agentic AI Chatbots
Action-oriented chatbots go beyond answering questions. They are designed to take actions.
In this model, the LLM acts as a reasoning layer that decides what to do, while tools and workflows execute those decisions. This is commonly referred to as agentic AI.
Typical capabilities include:
- Calling APIs
- Creating tickets or CRM records
- Scheduling meetings
- Triggering business workflows
Workflow engines like n8n are frequently used as the execution layer, enabling reliable integrations and auditable automation. Frameworks such as LangGraph or LangChain handle agent orchestration and decision flow.
This category is ideal for:
- Conversational AI agent development
- AI-powered process automation
- Real-world business task execution
Examples
- LangGraph or LangChain-based agents
- Botpress with custom actions
- Custom agents integrated with n8n workflows
3. Real-Time Conversational AI (Voice + Chat)
Real-time conversational AI focuses on how users interact with the chatbot rather than what it knows.
These systems are optimized for:
- Low-latency conversations
- Natural turn-taking
- Voice-first interactions
They support both voice and chat, making them suitable for customer support lines, outbound calling, and interactive voice agents. While they may be read-only or agentic, their defining feature is real-time conversation, not workflow complexity.
This category is increasingly relevant for:
- Real-time conversational AI experiences
- Voice-enabled support and sales
- Multi-channel AI agents
Examples
- VAPI
- Retell
These platforms are often combined with RAG systems or agentic logic to create full conversational AI agent development solutions.
4. Custom & Enterprise AI Chatbots
Custom and enterprise AI chatbots are not a separate capability—they are an implementation choice applied to the previous three categories.
Organizations choose custom or enterprise-grade builds when they need:
- Data ownership and isolation
- Security and compliance
- Integration with internal systems
- High performance cloud architecture
- Long-term scalability
These solutions are commonly built using serverless architecture consulting, cloud-native services, and enterprise-grade observability. They may combine RAG, agentic workflows, and real-time conversation depending on business needs.
Examples
- Azure Bot Service with Azure OpenAI
- Custom AWS or GCP chatbot deployments
- Regulated enterprise chatbot platforms
This approach is common for advanced cloud architecture consulting and large-scale generative AI solutions for enterprise environments.
How to Choose the Right Approach
Instead of asking “Which chatbot tool is best?”, ask:
- Do we only need answers from our data?
- Do we need the chatbot to take actions?
- Do we need real-time voice interaction?
- Do we need enterprise-grade control and compliance?
The answers naturally map to one or more of the four approaches above.
Final Thoughts
There is no single “best” AI chatbot. The right solution depends on capabilities, not buzzwords.
Most organizations start with a knowledge-grounded chatbot, evolve into agentic workflows, and later add real-time conversational AI or enterprise-grade architecture as requirements grow. Designing with this progression in mind helps avoid rework and ensures your chatbot scales with your business.








